Understanding Cholesterol: A Comprehensive Guide to Diet and Health
Delve into the intricacies of cholesterol and its relationship with diet and overall health.
Cholesterol, often misunderstood and sometimes demonized, plays a vital role in our bodies' functioning. However, when levels become imbalanced, it can pose significant health risks. Understanding cholesterol and its intricate relationship with diet and overall health is crucial for making informed decisions about our lifestyles. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of cholesterol, exploring its functions, types, sources, and the impact of diet on cholesterol levels.
Understanding Cholesterol:
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in every cell of the body and is essential for the production of hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids, which aid in digestion. Our bodies produce cholesterol naturally, primarily in the liver, but it is also obtained from the foods we eat. Cholesterol travels through the bloodstream in packages called lipoproteins, which are classified into two main types: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
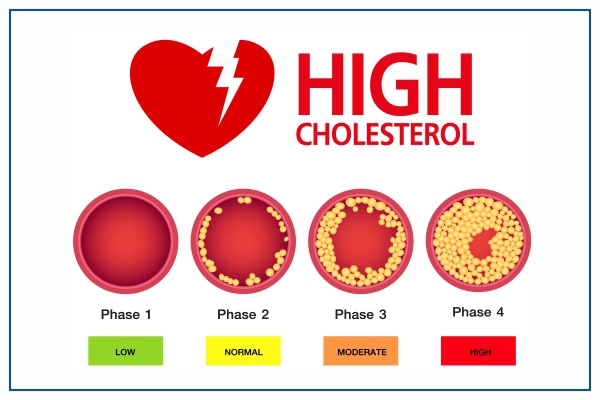
LDL cholesterol, often referred to as "bad" cholesterol, can build up in the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the narrowing and hardening of arteries. On the other hand, HDL cholesterol, or "good" cholesterol, helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Sources of Cholesterol:
Dietary cholesterol is found in animal-based foods such as meat, poultry, eggs, and full-fat dairy products. However, saturated and trans fats, rather than dietary cholesterol itself, have a more significant impact on blood cholesterol levels. Foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as fried foods, processed snacks, and baked goods, can raise LDL cholesterol levels.
The Role of Diet in Managing Cholesterol:
Maintaining a healthy diet is essential for managing cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of heart disease. The following dietary strategies can help:
Choose Healthy Fats: Replace saturated and trans fats with healthier options such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds. These fats can help raise HDL cholesterol levels while lowering LDL cholesterol.
Increase Fiber Intake: Foods high in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, fruits, and vegetables, can help lower LDL cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive system and removing it from the body.
Limit Dietary Cholesterol: While dietary cholesterol has less impact on blood cholesterol levels than saturated and trans fats, it's still essential to moderate intake from high-cholesterol foods.
Eat Fatty Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and trout are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help lower triglycerides and increase HDL cholesterol levels.
Adopt a Mediterranean Diet: The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, olive oil, and lean protein sources, has been shown to improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Be Mindful of Portion Sizes: Even healthy foods can contribute to weight gain and elevated cholesterol levels if consumed in excess. Pay attention to portion sizes and practice moderation.
Cholesterol plays a crucial role in our bodies, but maintaining a balance is key to good health. By understanding the relationship between cholesterol and diet, we can make informed choices to support heart health and overall well-being. Incorporating healthy fats, fiber-rich foods, and other heart-healthy choices into our diets can help manage cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Remember, small changes in diet and lifestyle can lead to significant improvements in cholesterol levels and long-term health outcomes.






