The Role of Hormones in Weight Regulation
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating appetite, metabolism, and body weight.
Weight regulation is a complex interplay of physiological processes orchestrated by a symphony of hormones. From signaling hunger and satiety to influencing metabolism and energy expenditure, hormones serve as pivotal messengers in the intricate dance of maintaining body weight and composition. Understanding the nuanced roles of these hormones is essential for unraveling the complexities of weight management and addressing the underlying factors that contribute to obesity and metabolic disorders. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve deep into the multifaceted role of hormones in weight regulation, uncovering their mechanisms of action and implications for overall health and well-being.
The Hormonal Orchestra
A diverse array of hormones governs various aspects of weight regulation, each playing a unique and complementary role in maintaining energy balance and metabolic homeostasis. Among the most influential hormones are:
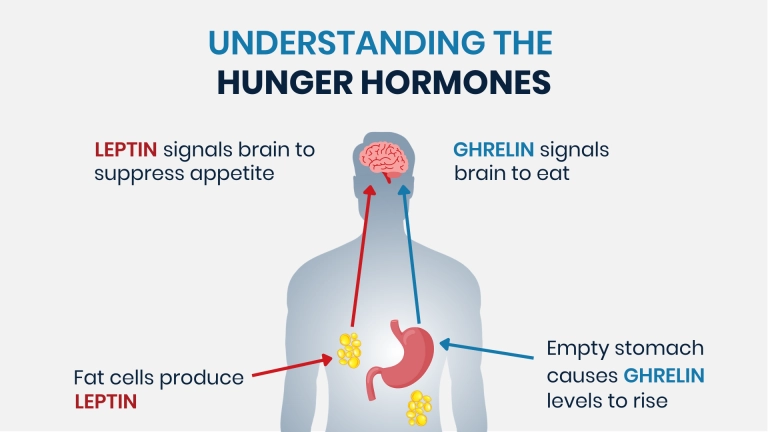
- Leptin: Widely recognized as the "satiety hormone," leptin is secreted primarily by adipose tissue and acts on the hypothalamus to regulate appetite and energy expenditure. By signaling the brain when energy stores are replete, leptin helps to suppress hunger and maintain body weight within a narrow range.
- Ghrelin: In stark contrast to leptin, ghrelin is dubbed the "hunger hormone" for its potent appetite-stimulating effects. Produced primarily in the stomach, ghrelin levels surge in anticipation of meals, triggering hunger pangs and promoting food intake. Ghrelin secretion diminishes after eating, contributing to the sensation of satiety.
- Insulin: Secreted by the pancreas in response to elevated blood glucose levels, insulin plays a central role in glucose metabolism and energy storage. Beyond its glucose-lowering effects, insulin facilitates the uptake of nutrients into cells, promotes glycogen synthesis in the liver and muscles, and inhibits lipolysis in adipose tissue.
- Cortisol: The body's primary stress hormone, cortisol is released by the adrenal glands in response to perceived threats or stressors. While acute cortisol elevation mobilizes energy reserves and enhances survival, chronic stress and sustained cortisol secretion can disrupt metabolic balance, promote abdominal fat deposition, and contribute to weight gain.
- Thyroid Hormones: Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), produced by the thyroid gland, exert profound effects on metabolism, energy expenditure, and body weight regulation. Thyroid hormones influence basal metabolic rate, thermogenesis, and lipid metabolism, exerting fine control over energy balance and metabolic rate.
Implications for Weight Management
Dysregulation of hormone levels can profoundly impact appetite regulation, metabolic function, and body composition, predisposing individuals to weight gain, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction. Lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, sleep quality, stress management, and underlying medical conditions can modulate hormone levels and influence weight regulation.
Practical Strategies for Hormonal Balance and Weight Management
To support hormonal equilibrium and optimize weight management, consider implementing the following evidence-based strategies:
- Embrace a Balanced Diet: Prioritize whole, nutrient-dense foods rich in fiber, lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates. A balanced diet promotes satiety, stabilizes blood sugar levels, and supports hormonal balance.
- Cultivate Stress Resilience: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or progressive muscle relaxation to mitigate cortisol release and promote relaxation.
- Prioritize Quality Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of restorative sleep per night to support hormonal balance, appetite regulation, and metabolic health. Establish a consistent sleep schedule, create a conducive sleep environment, and practice bedtime rituals to optimize sleep quality.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Incorporate a mix of aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises into your routine to promote metabolic health, muscle mass preservation, and weight management.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with a healthcare provider, registered dietitian, or endocrinologist if you suspect hormonal imbalances or underlying medical conditions affecting weight regulation. A comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan can address underlying factors and support your weight management goals.
Hormones wield significant influence over appetite, metabolism, and body weight, serving as integral players in the intricate tapestry of weight regulation. By understanding the nuanced roles of key hormones and implementing targeted strategies to support hormonal balance, you can optimize weight management and achieve sustainable success in your health and wellness journey. Prioritize lifestyle factors that promote hormonal health, cultivate resilience in the face of stress, and seek professional guidance when needed to navigate the complexities of weight regulation with confidence and empowerment. Remember, achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a holistic approach addressing both physiological and behavioral factors.






