The Importance of Fiber

Fiber is an essential nutrient that can aid in weight management by promoting feelings of fullness and supporting digestive health.
Amidst the myriad of nutrients that populate our dietary landscape, fiber stands out as a humble yet mighty ally in the quest for optimal health and weight management. Beyond its reputation as a digestive aid, fiber plays a multifaceted role in supporting satiety, regulating blood sugar levels, promoting heart health, and facilitating weight loss. In this article, we delve into the importance of fiber in our diet, exploring its diverse benefits and practical strategies for incorporating more fiber-rich foods into our daily meals.
The Crucial Role of Fiber
Fiber, a type of carbohydrate found exclusively in plant-based foods, encompasses a range of indigestible compounds that pass through the digestive tract largely intact. Unlike other carbohydrates, fiber remains undigested by enzymes in the small intestine, reaching the colon where it undergoes fermentation by beneficial gut bacteria. This unique journey through the digestive system confers numerous health benefits, including:
- Satiety Promotion: High-fiber foods possess bulk and viscosity, which can help increase feelings of fullness and satisfaction after meals. By slowing gastric emptying and prolonging the digestion process, fiber-rich foods contribute to reduced calorie intake and improved appetite control, supporting weight management efforts.
- Digestive Health Support: Fiber plays a pivotal role in maintaining regular bowel movements and preventing constipation by adding bulk to stool and promoting bowel motility. Adequate fiber intake can alleviate symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and diverticulosis, while also reducing the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Soluble fiber, found in foods such as oats, legumes, and fruits, forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract that slows the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream. This helps stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent rapid spikes and crashes, making fiber-rich foods particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Heart Health Promotion: Certain types of fiber, such as soluble fiber, have been shown to lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol particles and facilitating their excretion from the body. By reducing cholesterol absorption and promoting heart-healthy lipid profiles, fiber can help lower the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke.
Practical Strategies for Increasing Fiber Intake
To reap the full benefits of fiber and support overall health and weight management, consider incorporating the following practical strategies into your daily routine:
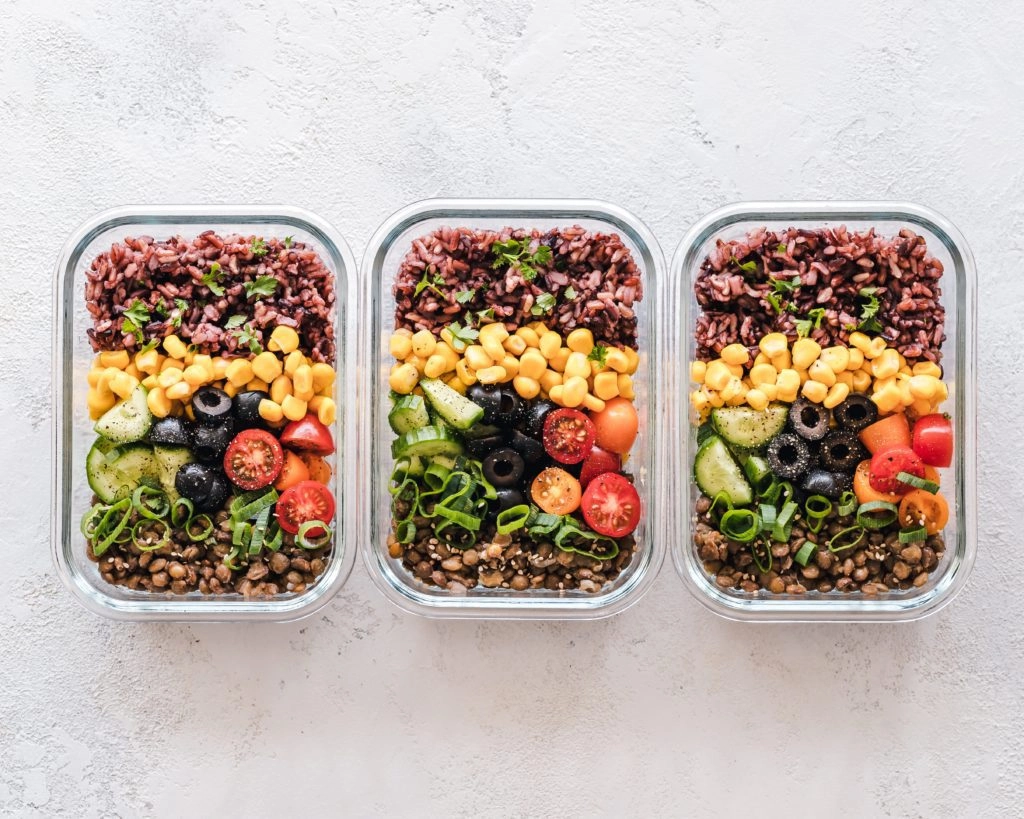
- Load Up on Whole Plant Foods: Focus on including a variety of whole plant foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods are naturally rich in fiber and provide a broad spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants essential for health.
- Choose High-Fiber Varieties: Opt for whole grains such as oats, barley, quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread and pasta, which retain their fiber-rich bran and germ layers. When selecting packaged foods, check the nutrition label for fiber content and choose products with higher fiber content per serving.
- Embrace Fruits and Vegetables: Incorporate a colorful array of fruits and vegetables into your meals and snacks to boost fiber intake and enhance nutritional diversity. Aim to fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables and include fruits as snacks or additions to meals.
- Incorporate Legumes: Include beans, lentils, chickpeas, and other legumes in your meals regularly to increase fiber intake and add plant-based protein to your diet. Experiment with different legume varieties and incorporate them into soups, salads, stews, and grain bowls.
- Snack Smart: Choose fiber-rich snacks such as raw vegetables with hummus, whole fruit, air-popped popcorn, or mixed nuts and seeds to satisfy hunger between meals while providing a nutrient boost.
- Gradually Increase Intake: Increase fiber intake gradually to allow your digestive system to adjust and minimize potential gastrointestinal discomfort such as bloating or gas. Aim to add an extra serving of fruits, vegetables, or whole grains to your meals each day until you reach your desired fiber intake.
Fiber is an indispensable nutrient with far-reaching benefits for health and weight management. By prioritizing fiber-rich foods in your diet and adopting practical strategies to increase fiber intake, you can support digestive health, promote satiety, stabilize blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Whether you're aiming to shed excess pounds, improve gastrointestinal function, or enhance overall well-being, fiber-rich foods offer a delicious and versatile way to nourish your body and optimize health from the inside out.